Welcome to LivingPianos.com, I’m Robert Estrin. Today’s subject is about lead sheets. Lead sheets are what jazz, rock, country, new age, and many other musicians play from. It’s simply the melody line and chord symbols rather than all the notes on the grand staff to be played by both hands. That’s what most working musicians read from, not the full score. As a matter of fact, other than Classical and perhaps Broadway musicals, the vast majority of music is not all written out note for note. The musicians kind of make up their part based upon the chord symbols and the melody line. So you might wonder: Did Classical musicians ever play from lead sheets? The answer is surprisingly, yes! Perhaps it’s a lost art, but let’s look back to the Baroque Era, with composers like Bach, Handel, Telemann, Corelli, and Vivaldi.
In the Baroque era music was written very differently.
With Baroque music, first of all, there were very few dynamics or phrasing indicated in the score. It was mostly just the notes, and that’s about it. Not only that, but you’ll notice ornamentation symbols throughout the score. These are squiggly lines that scholars, centuries later, are still trying to decipher what the composers meant by them. There are volumes of books written about how to approach mordents, trills and turns, as well as other ornamentation. The fact of the matter is, everybody has different ideas about them now. Back then, it’s likely that performers had the freedom to decide how much to embellish the score based upon these ornaments that were in the score. Perhaps they even added ornamentation in places that didn’t have any of these markings. There was a freedom to improvise on the music. But it goes much deeper than that.
Did you know that the trio sonata, which so many composers from Corelli to Telemann wrote hundreds of, were not actually completely written out?
Today, if you buy the sheet music to a trio sonata, it’s all written out. But it wasn’t originally written out. What is a trio sonata? A trio sonata was actually written for a solo instrument. It could be a violin. It could be a flute. It could be any instrument. And a basso continuo, which could be virtually any instrument playing the low part. Perhaps a cello, viola da gamba, something that could play the bass line, which was written out. So you had the melody and the bass written out. Well, what about the keyboard part, the harpsichord, in most cases back then? Was that part written out? No. Now, it wasn’t a lead sheet the way we think of a modern lead sheet. It was what’s called figured bass. Figured bass was a type of lead sheet notation, for lack of a better term.
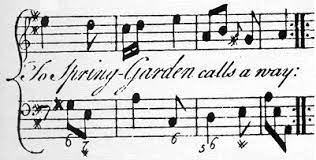
It did not have the notes. It just had chord symbols (in addition to the melody and bass line). The player had to realize the part based upon those symbols. They were improvising based upon chord changes, just like a jazz musician does today! This is the lost art of improvisation of the Baroque era.
Today when you buy sheet music for a Corelli or Telemann trio sonata it is all written out.
Somebody has gone to the trouble of realizing and writing out a keyboard part from those chord symbols of the figured bass. So almost nobody improvises anymore today. There are some early instrument enthusiasts who actually do this sort of thing. But for the most part, Classical musicians are so used to the sanctity of the score, that they don’t even realize that it wasn’t originally written out! These early works were not written out, except for the melody and the bass. The rest of it was left up to the performer to realize. And even the other parts could be embellished with ornamentation.
This is the truth about Classical music. It was much closer to modern styles of music than most people know. But today we look at it almost like pieces in a museum that you shouldn’t touch. They need to be preserved exactly as they were. But these were living, breathing works of music that evolved depending on who was performing them. So you want to approach Classical music in this way.
Cadenzas were originally improvised, not necessarily written out and learned.
The cadenza was a time for performers to showcase what they could do in the middle of a concerto, taking off on the themes that they had just played. Again, this is all but a lost art. During the Romantic period at salon concerts and informal gatherings, people would make up music going back and forth. They would try to outdo each other. This is what keeps Classical music alive and fresh, that spontaneous element. So while I certainly respect the scores of the great composers and fastidiously learn them, at the same time, you want to understand the lineage where this music comes from. You can add an element of spontaneity and inventiveness to your playing, realizing that these weren’t just static, etched-in-stone works. But they evolved, depending upon who was performing them!
I hope this has been interesting for you! Thanks so much for joining me, Robert Estrin here at LivingPianos.com, Your Online Piano Resource.
For premium videos and exclusive content, you can join my Living Pianos Patreon channel! www.Patreon.com/RobertEstrin
Contact me if you are interested in private lessons. I have many resources for you! Robert@LivingPianos.com
www.LivingPianos.com
www.Facebook.com/LivingPianos
949-244-3729
4 thoughts on “Did Classical Musicians Ever Play from Lead Sheets?”



Dear Robert,
The Novulette by Poulenc has three parts. HOW DO YOU MANGE WITH TWO HANDS ONLY, TO PLAY THE NOTES written on three scores on a normal piano?
Thank you,
Willene Botha
It’s not unusual for piano music to contain 3 or more parts. For example, in the 48 Preludes and Fugues of the Well Tempered Clavier of Bach, the fugues all contain 3 or more voices. Some of the fugues have as many as 5 voices (separate lines)! Usually they are contained within the 2 staves of the grand staff. This is typically done by having 2 or more parts in one staff, with one voice having stems going up, and one with stems going down. Sometimes the music can be written more clearly by spreading the notes out on to 3 staves. How the notes are negotiated depends upon the context of the writing. (Poulenc composed several Novelettes.)
Robert,
I was not aware of this.
Thank you for the on going information treasures.
Richard Rankin
So glad you find value in these presentations!